How to write academic documents with GoogleDocs
These past months I’ve been mostly working on one huge project which might be close to an end, hopefully! This project involves a massive manuscript with many supplementary figures and tables. Today we sent it out to other members in our team, and to celebrate, I’m now writing more 😅: though this is a blog post. I’m allowing myself to do so before I dive into the pile of tasks I haven’t completed1. So I’m going to share with you the tools I’ve been using since 2018 or so for writing academic documents shared via Google Docs. You can use these tools for manuscripts2, capstone projects3, and well, basically any document where you want to do any of the following:
- Automatic figure/table numbering
- Insert math equations
- Cite the literature
Yes, you can do both with LaTeX and you can collaborate with others using Overleaf, but it’s really hard to convince others to use LaTeX in my experience.
Citations
There are many tools out there for you to organize the literature items you are reading or keeping tabs on. Some of them are Zotero and Mendeley, which you might have heard about. The one that I highly recommend for writing documents with Google Docs is F1000Workspace.
Get an account
First, you need to make an account. Worried about paying? Don’t worry, the accounts are free4!

I strongly recommend that you use your academic email here if you have one, because I believe that it grants you access for an unlimited free account. Your university might also give you free access.
Start a project
Once you have your account set up, start a shared project. I mean, private ones also work, but shared ones allow you to collaborate with others so that your teammembers can also update the citations in your document. For example, we have one called brainseq phase2.
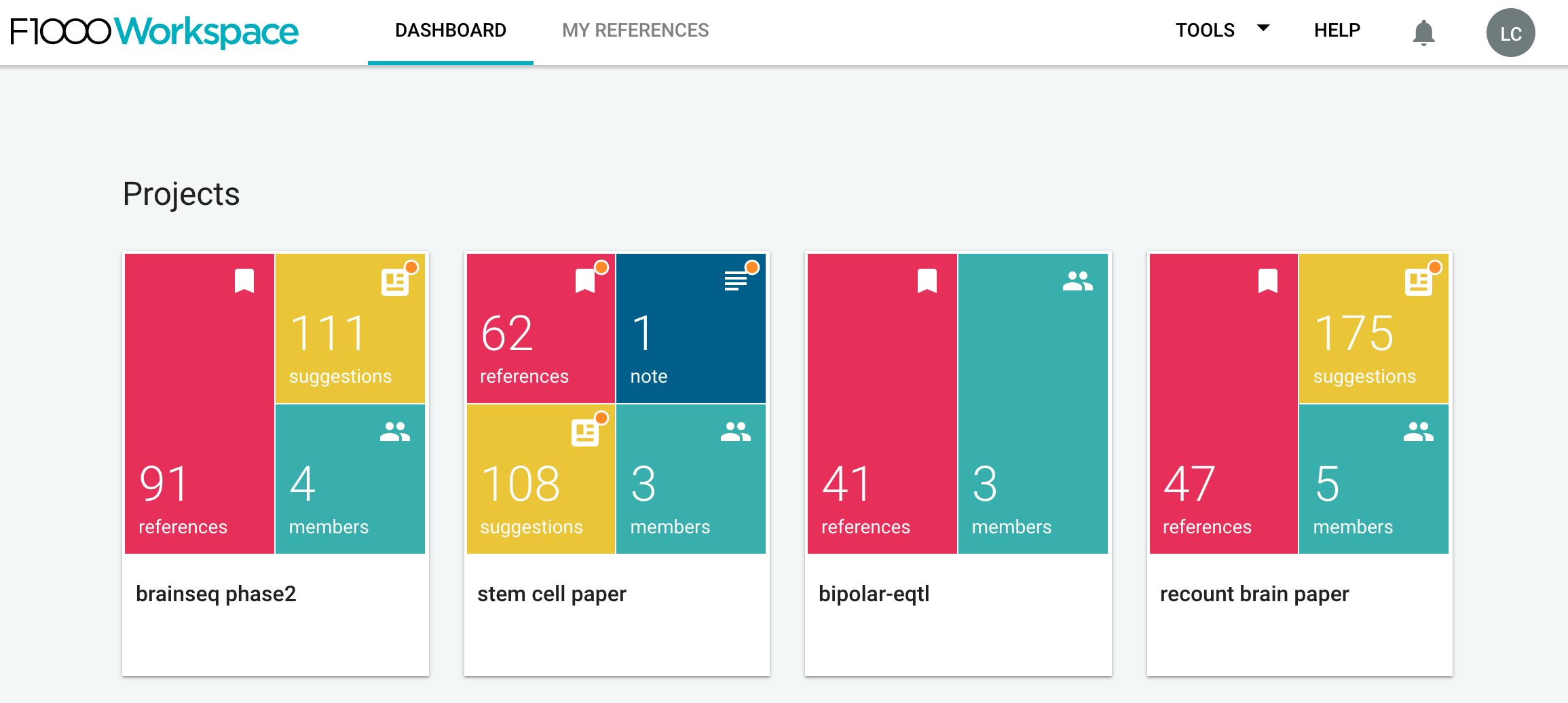
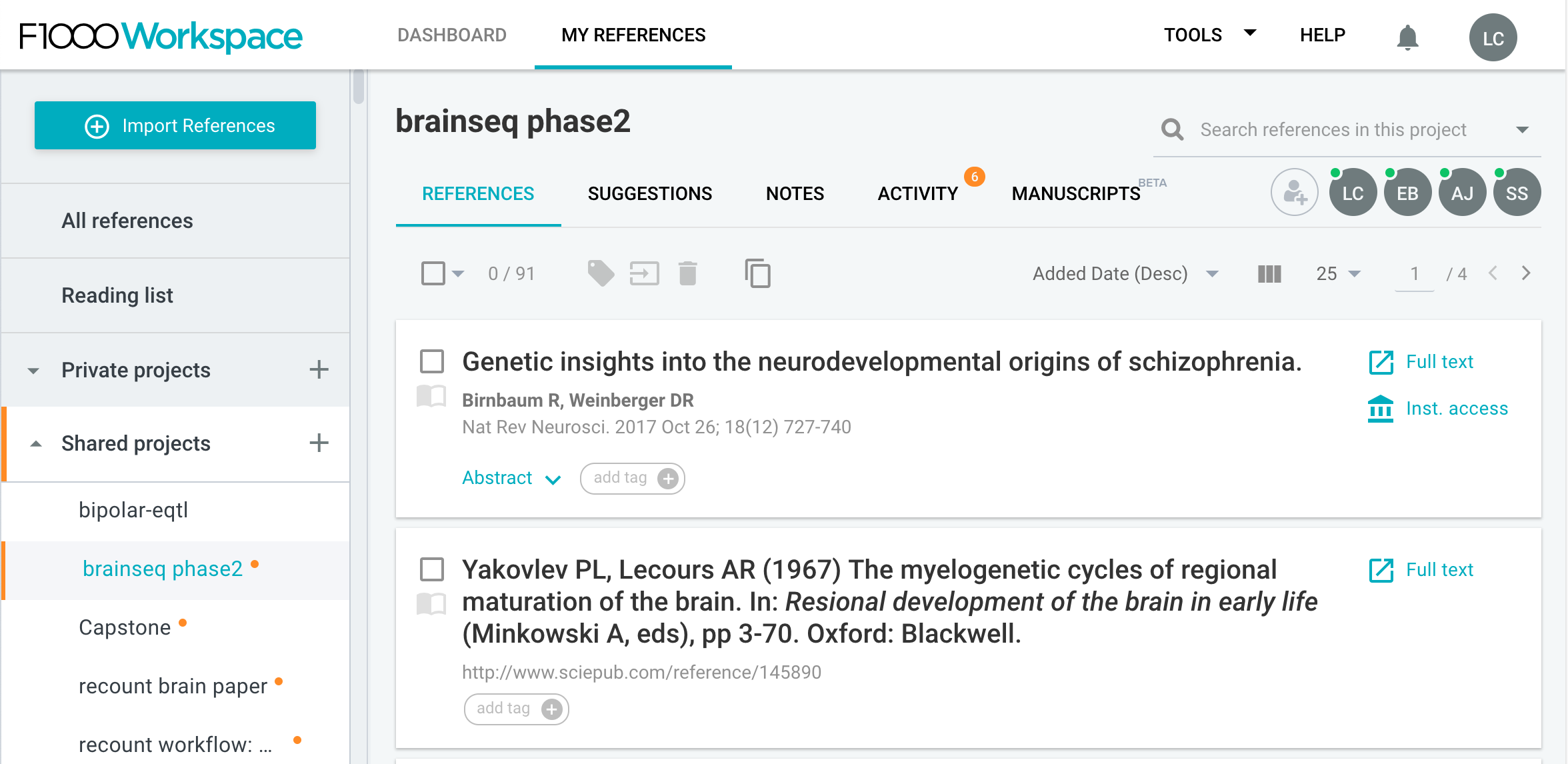
Once you open your project page, at the top left you’ll see a big blue button called Import References. Click on it.
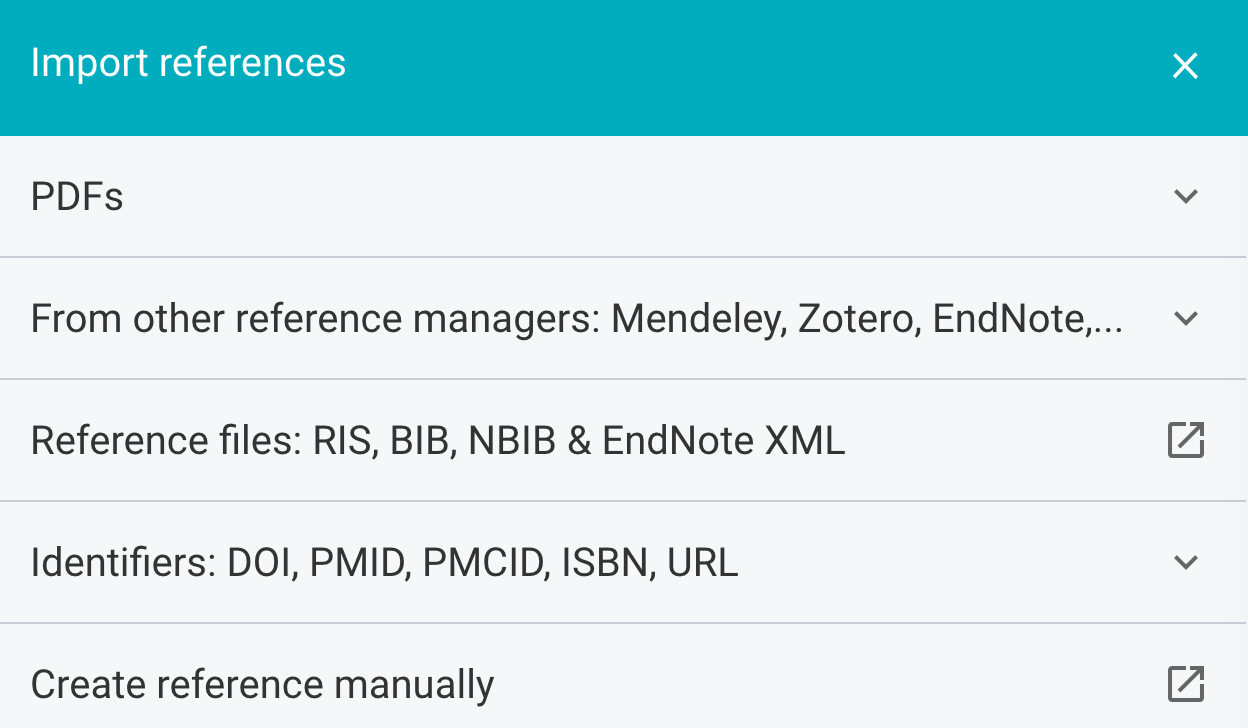
As you can see, F1000Workspace allows you to import references from many different sources. I typically import using identifiers, either a DOI or a PMID one. They also have a browser add-on that you can use to import references into your library when using websites such as PubMed.
Insert references into a Google Doc
On your Google Chrome browser, install the F1000Workspace Google Docs add-on available here. Next, open up your Google Doc and you’ll see that F1000 appears in your toolbar. If you click on it, the F1000 interface will open on the right sidebar.
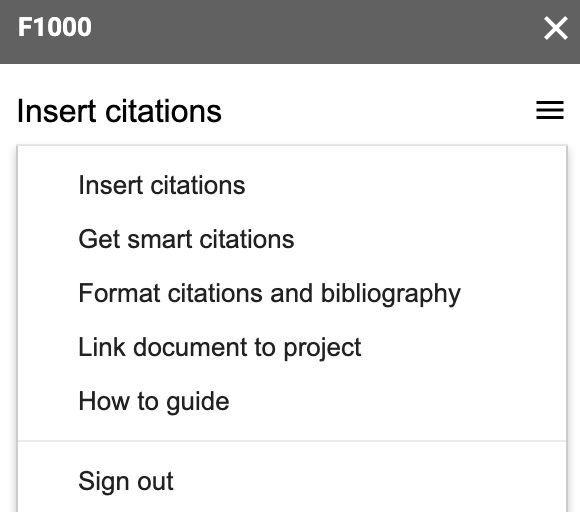
That interface lets you link your Google Doc to a particular F1000Workspace project, which I recommend doing. You can then go to Insert citations and start searching your project citations. I typically search by name or by the identifier, which is particularly useful if I just added the reference to the project via the identifier on a separate browser tab.
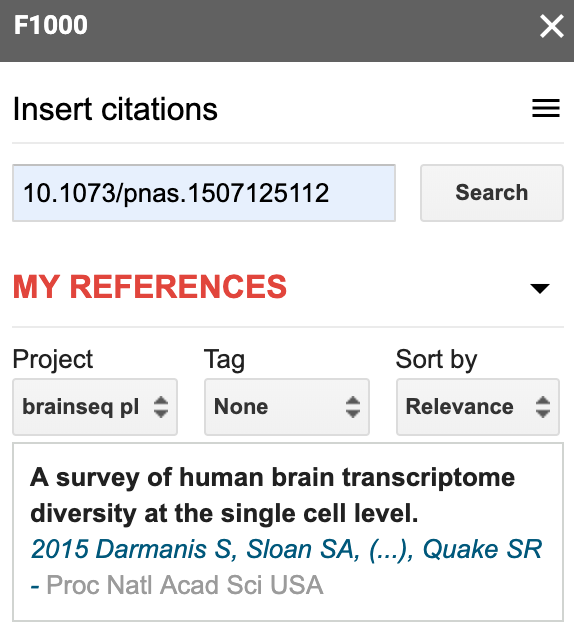
Update your document’s bibliography
Lets say that you’ve added a few citations in your document and now want to format them appropriately. In your Google Doc, click on F1000, then navigate to the Format citations and bibliography section.
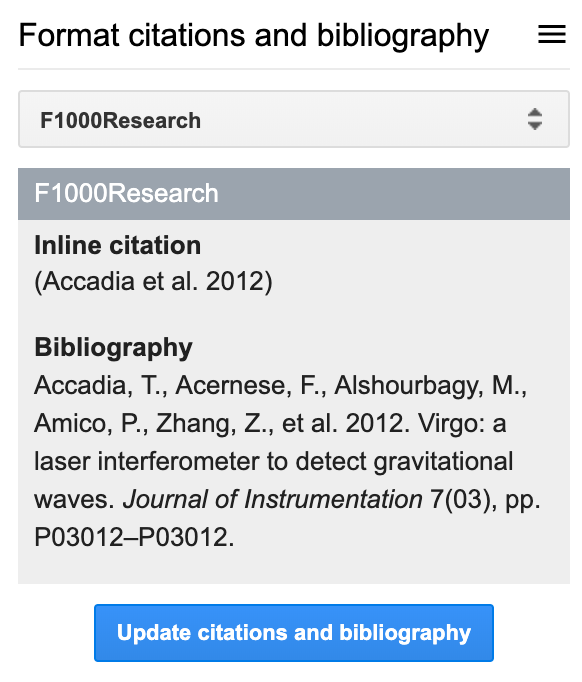
Before you click the big blue button that says Update citations and bibliography you’ll notice a dropdown menu that lets you choose your favorite citation style (or whichever the journal you want to send your manuscript requires).
The end!
Notes
Well, not really. You’ll likely keep adding many citations as you keep working on your document. One thing that I’ve noticed is that the F1000Workspace add-on has a bit of trouble under “suggesting” mode or when the citation was inserted as a suggestion. So I recommend that you accept the suggestion first, then use “editing” mode for updating your bibliography file. It’s always good to keep an eye on what the add-on is doing so you can notice anything weird and undo it with ctrl + z (cmd + z in macOS).
And hey, did you know that F1000Workspace also works with Microsoft Word?
For more details, check the FAQs.
Automatic figure numbering
Now that we have figured out citations in Google Docs, lets learn how to cross reference figures, tables, equations, and whatever else you want. This is something that LaTeX users are familiar with but that you can’t do out of the box in Google Docs or Microsoft Word (as far as I know). Luckily others have made add-ons that solve this problem. The one I use, and so do other 11,197 people as of today, is Cross Reference available from the Google Chrome Store for free.
This add-on allows the user to label equations, figures and tables and refer to them within the text. It now also allows users to create labels for any element. These elements are numbered automatically and references are updated to match. If their order changes, references update to match. If one is removed, references to it are highlighted in red in the text. The text and style of references and labels can be customised.
Insert labels and references as hyperlinks. Instead of a URL, add a code recognised by Cross Reference, then an underscore, then your choice of name.
Configuration
Once you install Cross Reference, you’ll see it listed under the Add-ons menu in your Google Doc.
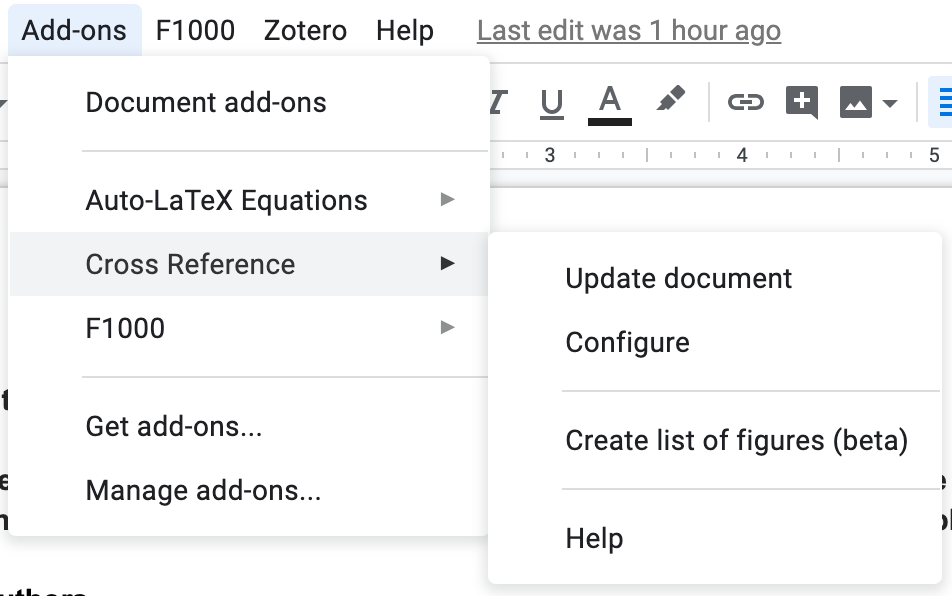
You’ll see all the different types of elements that you have configured with Cross Reference. Some come out of the box, like Figures.
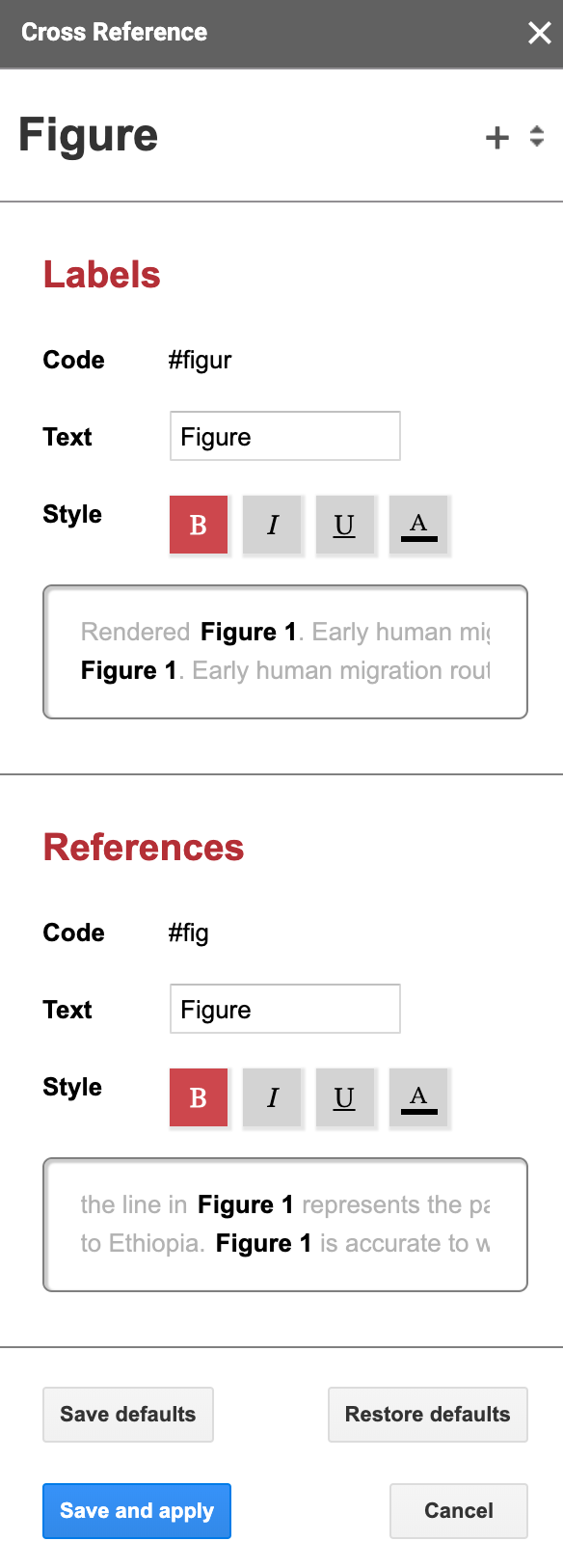
For every element you have to configure the following:
- The code you will use for the label, here
#figur. - The text that will be displayed before the number. In this case,
Figure(yes, there’s a space there). - The style of the label; bold here.
Then the same thing for the reference. In this case, the code for the reference is #fig. The codes have to be at least 3 characters long for the references and 5 characters long for the labels.
In my documents I typically add configurations for supplementary figures and tables using:
| type | code: label | code: reference | text |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplementary Figure | #sfigu |
#sfi |
Figure S |
| Supplementary Table | #stabl |
#sta |
Table S |
| Supplementary File | #supfi |
#sup |
Supplementary File |
Usage
Now that you have configured Cross Reference you can start using it. Lets say that I want to write the text We did many things (Figure S1) where Figure S1 links to my overview figure whose description starts Figure S1. Overview of my project. Since we are talking about the overview figure, lets use _overview as the unique identifier for this figure. As this is a supplementary figure, the label code is #sfigu and the reference code is #sfi. Meaning that we must write the label code once in the figure description using #sfigu_overview and we can reference to it as many times as we want using #sfi_overview.
The last tricky part is that you can write whatever you want, lets say hello, and then you need to create a link (shortcut is cmd + k in macOS) with the correct code (either the reference or the label one). So the text that you would write would be We did many things ([hello](#sfi_overview)) and later on when you describe the overview figure you need [whatever you want](#sfi_overview). Overview of my project where here I’m using the Markdown syntax for links: [text](link).
Once you’ve inserted the links both for the reference and the label, you can then go to Add-ons, navigate to Cross Reference and click Update document. Doing so will change the text you had initially filed in for the correct text. So it will look like this: We did many things ([Figure S1](#sfi_overview)) plus [Figure S1](#sfi_overview). Overview of my project. Here’s a real case example where my identifier for the first supplementary figure is _rna, thus the full reference code is #sfi_rna:

And you are done!
Notes
The number used for the item your reference depends on what order the reference codes are listed in the Google Doc. To check that the numbering order is correct (Table S1 appears in the text before Table S2, etc), I recommend opening your google document in two separate tabs. In one tab, you start reading your document from the top. If you encounter items out of order, then on tab two you can switch them around. That way you don’t have to scroll around and waste time, which is a more cumbersome problem as the document gets longer.
Overall, this process that takes a bit of time and can break due to a typo. So I highly recommend that you update your cross references as soon as you make a new one, so you can easily trace any typos and fix them easily. If you don’t, then it can become very hard to track down what went wrong.
Equations
Finally, lets say that you want to insert equations. You can insert some equations with Google Docs, but you might want more fine control. If you use LaTeX I recommend the Auto-LaTeX Equations add-on available from the Google Chrome Store for free.
This add-on lets you automatically convert every LaTeX equation in your document into beautiful images! Simply enclose your math equations within $$ … $$ and click the button in the sidebar, and all of your equations will be rendered in LaTeX!
It’s as simple as it sounds. What this add-on does is that it takes your LaTeX equation code, renders an image with the equation, and then inserts it back into your Google Doc. It also enables you to restore the LaTeX equation code so you can edit it if you find a typo.
Wrapping up
I hope that you’ll find this blog post / tutorial useful when writing your own academic documents. These tools have saved me so much time when writing academic documents in collaboration with others. I don’t want to imagine having to re-number all the references manually whenever we added each of the 48 supplementary figures, 17 supplementary tables, and 11 equations to the project we are about to complete 😱.
Acknowledgments
The authors of F1000Workspace, Cross Reference and Auto-LaTeX equations add-ons have made my life much easier. THANK YOU!!!
This blog post was made possible thanks to:
- BiocStyle (Oleś, 2023)
- blogdown (Xie, Hill, and Thomas, 2017)
- knitcitations (Boettiger, 2021)
- sessioninfo (Wickham, Chang, Flight, Müller et al., 2021)
References
\[1\] C. Boettiger. knitcitations: Citations for ‘Knitr’ Markdown Files. R package version 1.0.12. 2021. URL: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=knitcitations.
\[2\] A. Oleś. BiocStyle: Standard styles for vignettes and other Bioconductor documents. R package version 2.28.0. 2023. DOI: 10.18129/B9.bioc.BiocStyle. URL: https://bioconductor.org/packages/BiocStyle.
\[3\] H. Wickham, W. Chang, R. Flight, K. Müller, et al. sessioninfo: R Session Information. R package version 1.2.2. 2021. URL: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=sessioninfo.
\[4\] Y. Xie, A. P. Hill, and A. Thomas. blogdown: Creating Websites with R Markdown. Boca Raton, Florida: Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2017. ISBN: 978-0815363729. URL: https://bookdown.org/yihui/blogdown/.
Reproducibility
## ─ Session info ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## setting value
## version R version 4.3.1 (2023-06-16)
## os macOS Ventura 13.4
## system aarch64, darwin20
## ui X11
## language (EN)
## collate en_US.UTF-8
## ctype en_US.UTF-8
## tz America/New_York
## date 2023-07-11
## pandoc 3.1.5 @ /opt/homebrew/bin/ (via rmarkdown)
##
## ─ Packages ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## package * version date (UTC) lib source
## backports 1.4.1 2021-12-13 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## bibtex 0.5.1 2023-01-26 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## BiocManager 1.30.21 2023-06-10 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## BiocStyle * 2.28.0 2023-04-25 [1] Bioconductor
## blogdown 1.18 2023-06-19 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## bookdown 0.34 2023-05-09 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## bslib 0.5.0 2023-06-09 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## cachem 1.0.8 2023-05-01 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## cli 3.6.1 2023-03-23 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## colorout 1.2-2 2023-05-06 [1] Github (jalvesaq/colorout@79931fd)
## digest 0.6.31 2022-12-11 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## evaluate 0.21 2023-05-05 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## fastmap 1.1.1 2023-02-24 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## generics 0.1.3 2022-07-05 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## glue 1.6.2 2022-02-24 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## htmltools 0.5.5 2023-03-23 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## httr 1.4.6 2023-05-08 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## jquerylib 0.1.4 2021-04-26 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## jsonlite 1.8.7 2023-06-29 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## knitcitations * 1.0.12 2021-01-10 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## knitr 1.43 2023-05-25 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## lifecycle 1.0.3 2022-10-07 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## lubridate 1.9.2 2023-02-10 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## magrittr 2.0.3 2022-03-30 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## plyr 1.8.8 2022-11-11 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## R6 2.5.1 2021-08-19 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## Rcpp 1.0.10 2023-01-22 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## RefManageR 1.4.0 2022-09-30 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## rlang 1.1.1 2023-04-28 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## rmarkdown 2.23 2023-07-01 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## rstudioapi 0.14 2022-08-22 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## sass 0.4.6.9000 2023-05-06 [1] Github (rstudio/sass@f248fe5)
## sessioninfo * 1.2.2 2021-12-06 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## stringi 1.7.12 2023-01-11 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## stringr 1.5.0 2022-12-02 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## timechange 0.2.0 2023-01-11 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## xfun 0.39 2023-04-20 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## xml2 1.3.4 2023-04-27 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
## yaml 2.3.7 2023-01-23 [1] CRAN (R 4.3.0)
##
## [1] /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.3-arm64/Resources/library
##
## ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
-
Including answering some questions on the Bioconductor support forum, finishing another manuscript, etc. ↩︎
-
Like my former student Amy Peterson did in 2018. ↩︎
-
For up to 3 projects. ↩︎