Network nature of ligand-receptor interactions underlies disease comorbidity in the brain
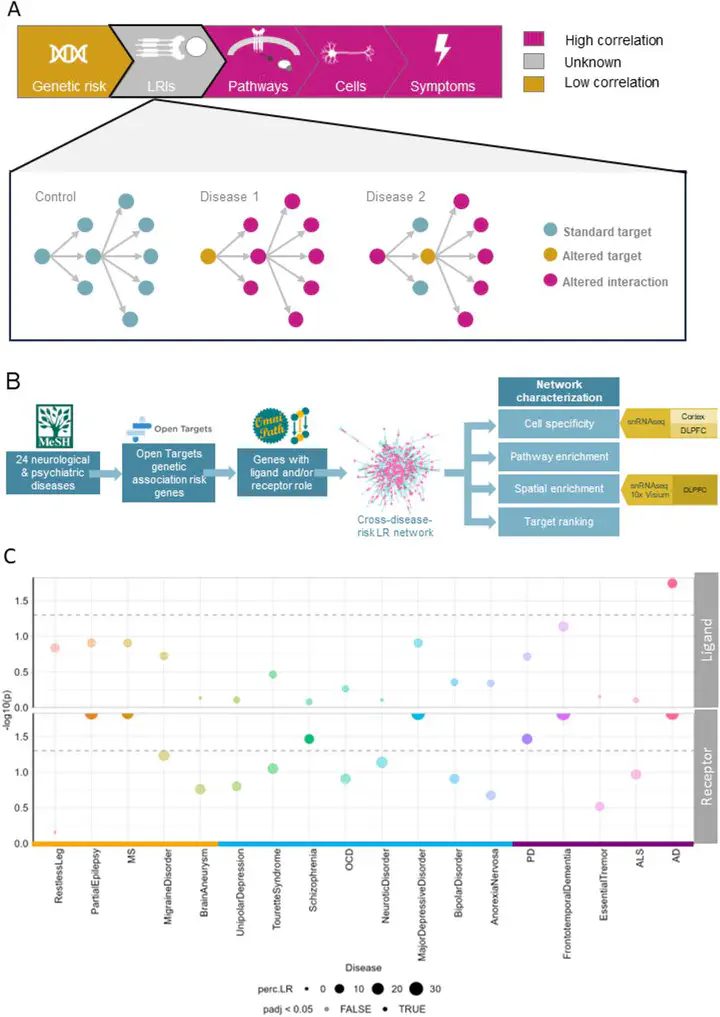 Image credit: bioRxiv
Image credit: bioRxiv
Abstract
Neurodegenerative disorders have overlapping symptoms and have high comorbidity rates, but this is not reflected in overlaps of risk genes. We have investigated whether ligand-receptor interactions (LRIs) are a mechanism by which distinct genes associated with disease risk can impact overlapping outcomes. We found that LRIs are likely disrupted in neurological disease and that the ligand-receptor networks associated with neurological diseases have substantial overlaps. Specifically, 96.8% of LRIs associated with disease risk are interconnected in a single LR network. These ligands and receptors are enriched for roles in inflammatory pathways and highlight the role of glia in cross-disease risk. Disruption to this LR network due to disease-associated processes (e.g. differential transcript use, protein misfolding) is likely to contribute to disease progression and risk of comorbidity. Our findings have implications for drug development, as they highlight the potential benefits and risks of pursuing cross-disease drug targets.