Spatiotemporal analysis of gene expression in the human dentate gyrus reveals age-associated changes in cellular maturation and neuroinflammation
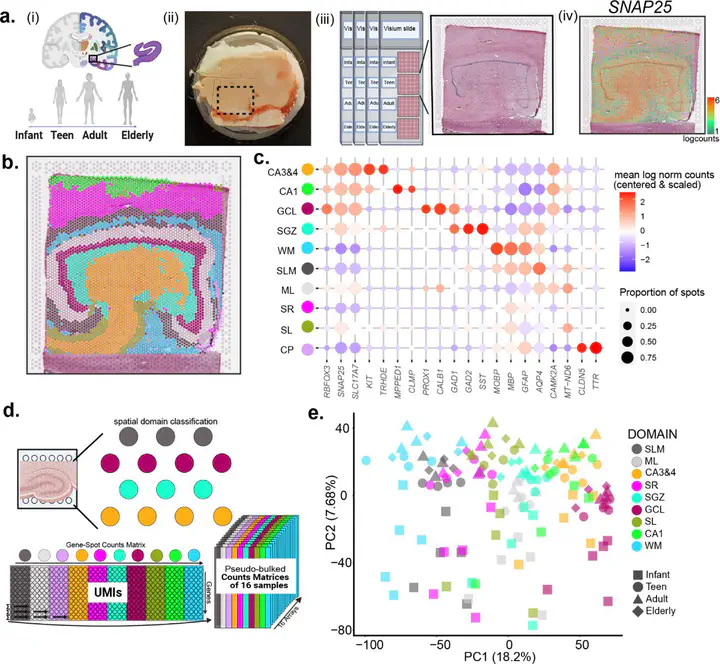 Image credit: bioRxiv
Image credit: bioRxiv
Abstract
The dentate gyrus of the hippocampus is important for many cognitive functions, including learning, memory, and mood. Here, we present transcriptome-wide spatial gene expression maps of the human dentate gyrus and investigate age-associated changes across the lifespan. Genes associated with neurogenesis and the extracellular matrix are enriched in infants and decline throughout development and maturation. Following infancy, inhibitory neuron markers increase, and cellular proliferation markers decrease. We also identify spatio-molecular signatures that support existing evidence for protracted maturation of granule cells during adulthood and age-associated increases in neuroinflammation-related gene expression. Our findings support the notion that the hippocampal neurogenic niche undergoes major changes following infancy and identify molecular regulators of brain aging in glial- and neuropil-enriched tissue.